
| Name: DPPA5 | Sequence: fasta or formatted (116aa) | NCBI GI: 70608179 | |
|
Description: developmental pluripotency associated 5
|
Referenced in: Stem Cells and Early Development
| ||
|
Composition:
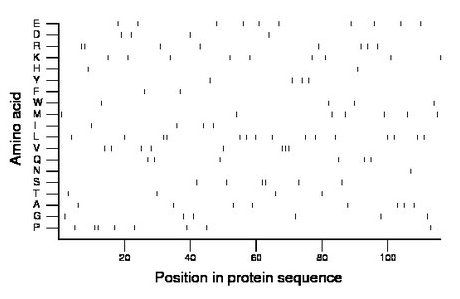
Amino acid Percentage Count Longest homopolymer A alanine 6.9 8 1 C cysteine 0.0 0 0 D aspartate 3.4 4 1 E glutamate 8.6 10 1 F phenylalanine 1.7 2 1 G glycine 5.2 6 1 H histidine 1.7 2 1 I isoleucine 3.4 4 1 K lysine 7.8 9 1 L leucine 12.9 15 2 M methionine 6.0 7 1 N asparagine 0.9 1 1 P proline 6.9 8 2 Q glutamine 5.2 6 1 R arginine 6.9 8 2 S serine 5.2 6 2 T threonine 3.4 4 1 V valine 6.9 8 3 W tryptophan 3.4 4 1 Y tyrosine 3.4 4 1 |
Comparative genomics:
Search single species RefSeq proteins at NCBI
Search summary 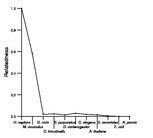
Figure data | ||
Related human proteins:Protein Relative score Description Self-match 1.000 developmental pluripotency associated 5 OOEP 0.188 oocyte expressed protein homolog C6orf221 0.164 hypothetical protein LOC154288 LOC100129128 0.047 hypothetical protein LOC100129128 KHDC1 0.023 KH homology domain containing 1 PLEKHA6 0.023 phosphoinositol 3-phosphate-binding protein-3 DSEL 0.009 dermatan sulfate epimerase-like PLEKHG3 0.009 pleckstrin homology domain containing, family G, mem... SPTBN1 0.009 spectrin, beta, non-erythrocytic 1 isoform 2 SPTBN1 0.009 spectrin, beta, non-erythrocytic 1 isoform 1 USP34 0.009 ubiquitin specific protease 34 STK33 0.009 serine/threonine kinase 33 LOC100292136 0.005 PREDICTED: hypothetical protein LOC100287246 0.005 PREDICTED: hypothetical protein LOC100287246 0.005 PREDICTED: hypothetical protein XP_002342513Human BLASTP results (used to prepare the table) | |||
Gene descriptions are from NCBI RefSeq. Search results were obtained with NCBI BLAST and RefSeq entries. When identical proteins are present, the self-match may not be listed first in BLASTP output. In such cases, the table above has been reordered to place it first.
See About the Figures for the scoring system used in the figure above right. The same scoring system was used in the table of BLASTP results.
Guide to the Human Genome
Copyright © 2010 by Stewart Scherer. All rights reserved.
